Introduction
Diabetes is a chronic medical condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the body is unable to properly regulate blood sugar (glucose) levels due to insufficient insulin production or the body’s inability to use insulin effectively. If left unmanaged, diabetes can lead to severe health complications. This blog explores the causes, symptoms, and management of diabetes to help individuals gain a better understanding of this condition.
Types of Diabetes
There are three main types of diabetes:
- Type 1 Diabetes – An autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. It typically develops in childhood or adolescence and requires insulin therapy.
- Type 2 Diabetes – The most common form, often linked to lifestyle factors such as obesity and inactivity. The body either does not produce enough insulin or cannot use it effectively.
- Gestational Diabetes – Occurs during pregnancy and usually resolves after childbirth. However, it increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Causes of Diabetes
Several factors contribute to the development of diabetes:
- Genetic predisposition – A family history of diabetes can increase the risk.
- Obesity – Excess body fat, especially around the abdomen, is a major risk factor for type 2 diabetes.
- Sedentary lifestyle – Lack of physical activity reduces insulin sensitivity.
- Unhealthy diet – High intake of processed foods, sugary beverages, and refined carbohydrates can lead to insulin resistance.
- Hormonal changes – In the case of gestational diabetes, hormonal shifts during pregnancy can affect insulin function.
Symptoms of Diabetes
Common symptoms of diabetes include:
- Frequent urination
- Excessive thirst and hunger
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue and weakness
- Blurred vision
- Slow healing of wounds
- Numbness or tingling in hands and feet
Management and Prevention
While diabetes has no cure, it can be effectively managed through lifestyle changes, medication, and regular monitoring.
1. Healthy Eating
- Focus on a balanced diet rich in whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, and vegetables.
- Limit sugar intake and processed foods.
- Maintain portion control to avoid overeating.
2. Regular Exercise
- Engage in at least 30 minutes of moderate activity, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, most days of the week.
- Strength training helps improve insulin sensitivity.
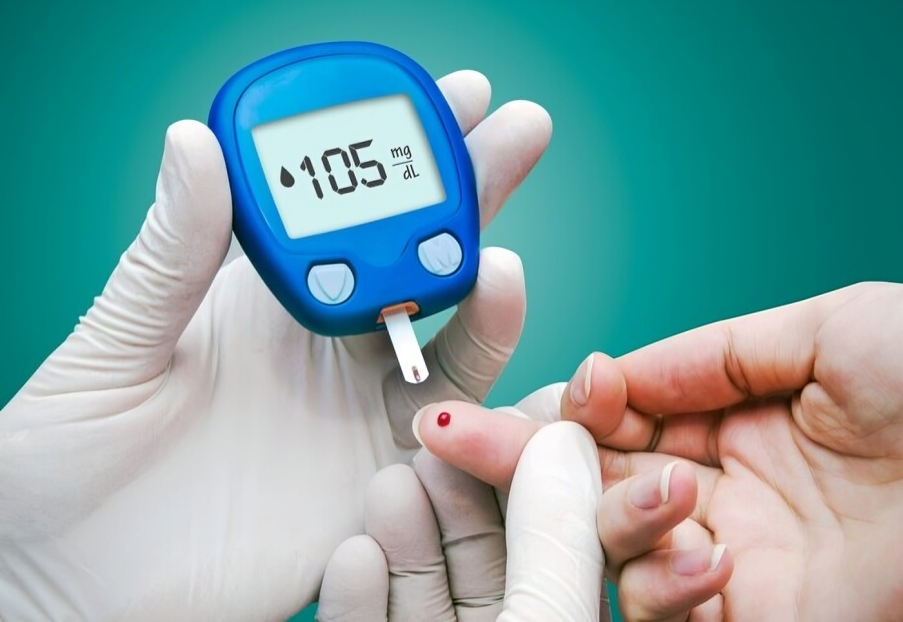
3. Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
- Regularly check blood glucose levels to ensure they are within the target range.
- Keep track of food intake and activities that may affect sugar levels.
4. Medication and Insulin Therapy
- Type 1 diabetes requires insulin injections or an insulin pump.
- Type 2 diabetes may be managed with oral medications or insulin, depending on severity.
5. Stress Management and Sleep
- Chronic stress and lack of sleep can impact blood sugar levels.
- Practice relaxation techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
Conclusion
Diabetes is a serious but manageable condition with the right lifestyle choices and medical interventions. By maintaining a healthy diet, staying active, and monitoring blood sugar levels, individuals can lead a fulfilling life while keeping diabetes under control. If you suspect you have diabetes or are at risk, consult a healthcare professional for early diagnosis and appropriate treatment.